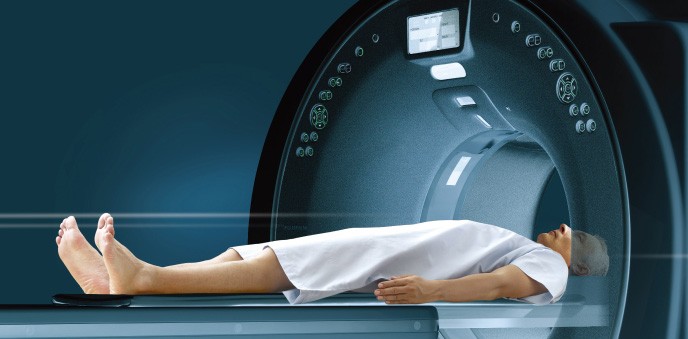
What is CT scan?
CT scan, a computerized tomography, provides more detailed information about the human body. It involves taking X-ray images of the body from different angles using computer processing and obtaining cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body.
Why experts recommend CT scan?
This diagnostic measure helps quick examination of internal injuries due to accidents or falls. It facilitates diagnosing disease or injury and accordingly planning a medical, surgical, or radiation treatment.
How a CT scan is done?
The procedure needs the patient to lie down in a narrow, motorized table that slides through the opening into a tunnel. Straps and pillows help the person to stay in the position. The scanner, detectors, and the X-ray tube rotate around the person while he lies still in the bed. Each rotational round produces a buzzing sound and generates a thin slice of the body. Technologists sitting at a distance can see, hear and communicate with the person through an intercom. They may instruct the person to hold a breath, lie still to avoid image blurring.
Why Contrast Dye is used in a CT scan?
Sometimes technologists make use of contrast dyes to highlight the area of the body that needs diagnosis. Contrast material blocks X-rays and appears white on images. There are three ways of injecting contrast dye into the body.
Scanning of the stomach, oesophagus needs a person to drink contrast dye through the mouth. Technologists inject contrast dye through injection in the vein of an arm for a CT scan of the gallbladder, urinary tract, liver, or blood vessels. For visualization of intestines, experts may inject a contrast dye into the rectum.
After Results
The procedure of a CT scan does not restrict a person from continuing his routine activities. However, a CT scan with contrast dye needs a person to wait for a few hours after the CT scan. He may need to follow a set of instructions like drinking a lot of water to help Kidneys eliminate dye from the body. CT scan images produce electronic data on the computer screen. A radiologist interprets these images, prepares a report, and sends it to the doctor.
Good physician treats the disease
- Pulmonary Angiography
- Renals (Kidneys) Angiography
- Neuro-DSA / Brain Angiography
- Peripheral Angiography
- Head(3D)
- Orbit(3D)
- Paranasal Sinuses (3D)
- Petrous Temporal (3D)
- Neck (3D)
- Lumbo-sacral (3D)
- Chest/ HRCT Chest (3D)
- Whole Abdomen / Pelvis (3D)
- Upper Abdomen/ Pelvis (3D)
- Others (in 10 sec)
- Whole Body 3D CT Scan
- Whole Body Digital X-ray
- IVP and HSG
- Barium Studies



