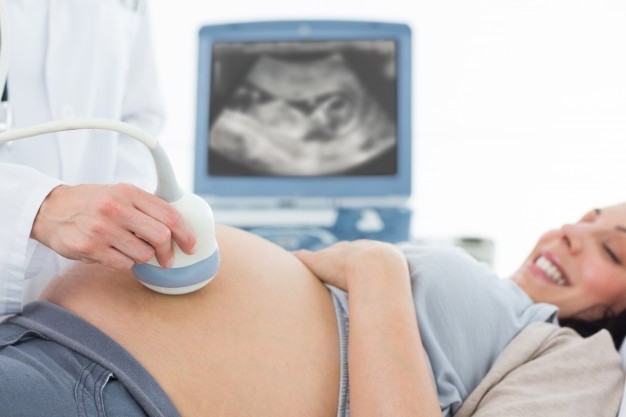
What is Ultrasound Scanning?
Ultrasound scans use high high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. The technical diagnostic procedure is painless that experts use to examine internal organs in a detailed manner.
Who needs Ultrasound Scanning?
The sonography procedure is safe and uses low-pressure sound waves to produce an image of body organs. However, it does not image body parts having gas in them or is behind bones, such as the lungs or head. Treatment for such organs requires a person to undergo other imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans or X-rays.
How it is done?
The sonographer applies gel on the part of the body which, needs an ultrasound image. The gel prevents air blocking, which can block the sound waves that create the images. Rubbing the transducer on the area under observation produces images on the computer. The device collects the sound waves and bounces back, sending them to the computer and generating ultrasound images.
Sometimes there arises the insert transducer into the body. Transesophageal echocardiogram needs inducing transducer into the oesophagus to obtain heart images. A transrectal ultrasound needs to insert a transducer through the rectum to get scan images of the prostate. Transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting the instrument into the vagina to scan the uterus and ovaries.
After the process
Completion of the process takes 30 minutes to an hour. The procedure is painless. However, one may experience mild discomfort if there is a need for inserting a transducer into the body. Radiologists analyze the images prepare the reports and send them to the concerned doctor for recommending treatment options.
Good physician treats the disease
- 4D - 3D Voulme Scanning
- NT Scan (11 t0 14 Weeks)
- Foetal echocardiography
- High Resolution Color Doppler
- US Guided FNAC
- TRUS / TVS Sonography
- Ovulation Monitoring
- Breast/ Testes/ Thyroid/ Eye-Orbit
- Carotid and Peripheral Vascular Doppler
- Penile Doppler
- Neonatal Neuro-Sonography & Chest
- Musculoskeletal Sonography
- 3D mapping for Firoids



